Process Overview
Adopting the latest Technology for Efficient and Reliable Manufacturing

Process of heating metal without letting it reach its molten state and then cooling it in a controlled manner to achieve desired mechanical properties. The Heat Treatment consists of :
a) Heating cycle in which the part is heated at a consistent rate till a certain temperature
b) Soaking cycle in which the part is held at a particular temperature
c) Cooling cycle in which the part is cooled using different cooling media to achieve the desired properties. The cooling cycle is the most crucial stage of HT cycle as it determines the final grain structure thereby influencing the mechanical properties of the metal. Heat Treatment is broadly classified as Bulk and Surface Heat Treatment.
Few common Bulk Heat Treatment process performed by us are :
These processes are used to refine and homogenize the grain structure to remove residual stresses and improve machinability. The only difference between Annealing and Normalizing is the former is furnace cooled and the other is air cooled.
The purpose of hardening is to increase the hardness of steel by producing a fully martensitic structure through controlled cooling rate whereas tempering is to relieve the residual stresses induced during hardening and improve toughness and ductility of steel. Hardening is mainly characterized by composition of alloy, type of quenching medium and size and shape of part.
Few common Surface Heat Treatment process performed by us are :
It is a thermochemical process in which carbon is diffused into the surface of low carbon steels to increase the carbon content to sufficient levels so that the surface will respond to heat treatment and produce a hard, wear-resistant layer.
It is a thermochemical process in which nitrogen is diffused in alloy steel to form a hard surface. It is further classified as Gas, Liquid and Plasma nitriding based on the media being used.
It involves diffusion of both carbon and nitrogen into the surface of steel substrate.
Materials
Commodities that we emulsify into Finished product
During Heat Treatment the steel undergoes rapid phase transformation at different temperatures with each phase exhibiting a certain characteristic. The heat cycle followed for each grade of steel varies due to its chemical composition and the graph formed as a result is called TTT (Time Temperature Transformation) graph. The commonly appearing phases in heat treatment are Ferrite, Austenite, Pearlite, Cementite, Bainite and Martensite. Each of these phases can be clearly distinguished at microscopic level. Commonly metals which are heat treated are :
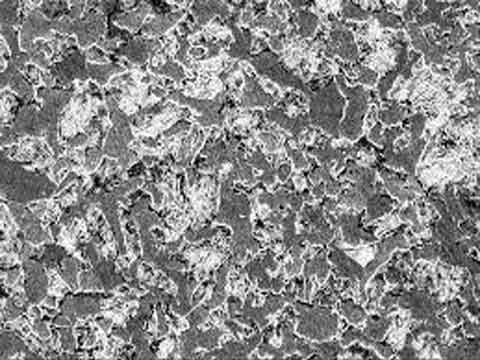
Carbon Steel
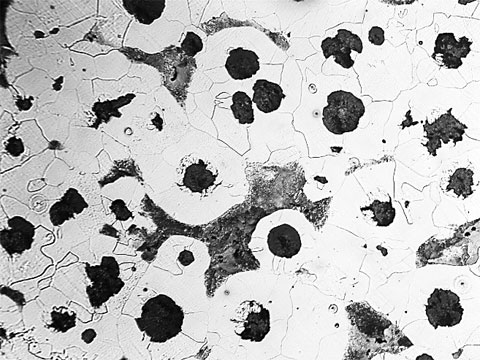
Cast Iron
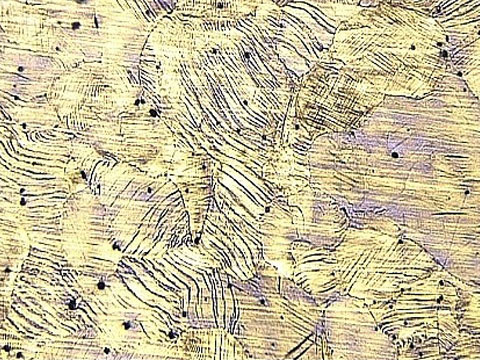
Alloy Steel
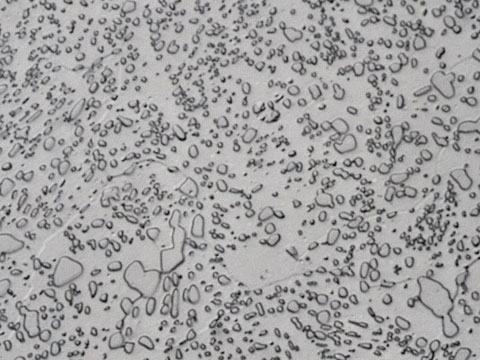
Tool Steel
Capabilities
A synopsis of our Skills and Expertise
- All heat treatment processes under one roof
- Completely automated and PID controlled heat treatment furnaces
- Paperless recording of heat treatment cycle with complete traceability
- Multiple furnaces to cater mass production
- Flexibility to load batch and production parts
- Vertical furnace up to 2 meter Dia and 8 meter height for loading of long shafts and rollers
- Heat treatment of raw as well as machined parts
- In-house and third-party testing of heat treated material for verification of required mechanical properties
- Heat Treatment facility certified to ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 Quality Management System
- Periodic calibration, maintenance, leak testing and temperature uniformity survey to ensure process reliability and consistency
Application and Benefits
Gain an Advantage over your Competition


- Heat Treated steels are used in almost every industry sector such as Aerospace, Automotive, Oil & Gas, Power Generation, Steel, Pumps and Valves, Hydraulic, Air and Gas Compressor, Construction etc.
-
Heat Treatment is the most effective and efficient method of achieving the desired mechanical properties by altering the grain structure of a conventional steel. Few advantages of Heat Treatment are as follows :
- Improving wear and corrosion resistance
- Improve fatigue strength
- Improve toughness
- Increase machinability by improving malleability and ductility
- Improve cold press property
- Improve other properties such as magnetic, thermal, and electrical properties
Frequently Asked Questions
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers!
- It is a thermal process in which the metal is heated above its re-crystallization temperature without letting it reach its molten stage and then cooling the metal in a controlled environment to alter its physical and sometimes chemical properties.
- Heat treatment is usually done to make a metal stronger, more malleable, resistant to abrasion or ductile.
- The three main stages in heat treatment are Heating, Soaking and Cooling.
- The purpose of heat treatment is to improve wear resistance, fatigue strength, machinability, cold press property, other physical properties such as magnetic property etc.
- The Fe - C diagram (also called the iron - carbon phase or equilibrium diagram) is a graphic representation of the respective microstructure states of the alloy iron - carbon (Fe-C) depending on temperature and carbon content. It is a universal diagram as it covers all Fe-C alloys.
- The various phases which exist in Fe – C diagram include ferrite, cementite, austenite, pearlite, ferrite + austenite and austenite + cementite.
- The Fe – C diagram considers very slow cooling or equilibrium cooling.
- If solubility of carbon is more than 2% in iron, it is theoretically called as cast iron. Balance carbon is present in free form in the form of granules or flakes.
- Ferrite – Interstitial solid solution of carbon in iron of body centered cubic crystal structure. The stability of this phase ranges between 1394 - 1539°C. This is not stable at room temperature in plain carbon steel. However, it can be present at room temperature in alloy steel, especially duple stainless steel.
- Austenite – Solid solution of carbon in FCC iron formed by solidification of liquid, large grains, and straight grain boundaries, stable at high temperatures. It has high solubility for carbon, high ductility, and formability. It has more solid solubility and density that ferrite. Its single-phase FCC structure is ductile at high temperatures. Large amounts of Ni and Manganese can be dissolved in FFC iron.
- Cementite – It contains 6.67% carbon by weight, and it is a metastable phase. It is typically hard and brittle interstitial compound of low tensile strength (approx. 5000 Psi) but high compressive strength. It is the hardest structure that appears on the Fe – C diagram. Its crystal structure is orthorhombic.
- Pearlite – It is composite structure of laminar ferrite and cementite, formed as a product of eutectoid transformation from austenite. It is not a phase but combination of two phases. It has a good, combined strength and toughness and ideal for structural applications.
- It stands for “Time Temperature Transformation” diagram. It is also called as isothermal transformation diagram and is used for identifying non-equilibrium structures produced in processing at realistic cooling rates.
- In Fe – C alloys, austenite transforms to martensite on rapid cooling. It is a non-equilibrium structure. It is a diffusion less transformation. Because of the rapid cooling, diffusion is suppressed, and carbon does not partition between ferrite and austenite.
- Factors affecting TTT diagram are composition of steel (carbon wt%, alloying element wt%), grain size of austenite, heterogeneity of austenite.
- Heat treatment process is broadly classified as Bulk heat treatment or Through hardening and Surface heat treatment or Case hardening.
- The various types of heat treatment process that we can undertake for your parts are annealing and normalizing, hardening and tempering, carburizing, nitriding, carbonitriding etc. For more details, please refer the Overview section of this page.
-
Depending on how fast the steel must be quenched, the heat treater will determine the type of quenching required :
- Air/Gas – It is gentler than oil and has less chance of producing internal stresses, distortion and cracks. It is generally used on steels which have very high alloy content.
- Water – It is the most used quenching media which is inexpensive and convenient to use. It provides very rapid cooling and can cause internal stresses, distortion, and cracking. It is especially used in low carbon steel which requires a very rapid change in temperature to obtain good hardness and strength.
- Oil – It is gentler than water and used for critical parts with thin sections and sharp edges such as razor blades, springs, sharp blades etc. It has less chance of producing internal stresses, distortion, and cracking. It is more effective when heated slightly above room temperature.
- Brine – It is usually made up of 5 to 10% solution of salt in water. It discourages the formation of air globule when it is placed in contact with heated metal. It has the fastest cooling rate and the ability to throw the scale from steel during quenching.
- Polymer – It is made up of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) with different concentration in water. It has faster cooling than oil and used for parts which cannot be properly quenched by oil. It can give excellent results on plain carbon and alloy steels that require superior depth of hardness and uniform, repeatable mechanical properties.
- We have developed and keep upgrading our capabilities by adding professional and experienced vetted suppliers to our vendor network. Please refer to Capability section of this page for more details.
- Tensile test – It is mechanical testing of a machined or full section specimen under examination to a measured load sufficient to cause rupture and is defined by ASTM E8 – Standard test method for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. It helps in determining various mechanical characteristics such as ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and reduction of area.
- Hardness test – It is used to determine the ability of a material to resist wear, abrasion, penetration, deformation, and machining. Three commonly used hardness test methods are Brinell hardness, Rockwell hardness and Vickers micro-hardness test.
- Chemical composition analysis – It is performed using Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES). A sufficient voltage is induced to produce an arc between a tungsten electrode and the sample to be analyzed. As a result of the burn induced on the sample, light is emitted from the sample. Each element in the sample produces a characteristic wavelength which is measured by the spectrometer. The intensity of each wavelength is directly proportional to the concentration present. Results are displayed in weight percent for each element chosen to be analyzed.
- Microstructure analysis – This is done to analyze the grain formation and its structure, presence of impurities, porosity, and other microscopic parameters.